Most companies today rely on a mix of cloud-based tools to manage their daily operations. You might use one platform for marketing, another for customer support, and a third for billing or analytics. While each tool has its own strengths, switching between them or updating information manually quickly becomes inefficient.
That’s where SaaS integrations come in. By connecting your software tools so they share data and trigger actions automatically, integrations help create a single, connected system that works behind the scenes.
This article breaks down what SaaS integrations are, how they work, the types you’ll encounter, and the challenges and benefits of setting them up. Whether you run a small startup or manage a large enterprise stack, understanding SaaS integrations can help you get more value out of the tools you already use.
What is a SaaS integration?
A SaaS integration connects two or more cloud-based applications so they can share data and work together automatically. Instead of switching between tools or re-entering information, integrations let data move between systems in real time.
For example, connecting your CRM with your email deliverability solutions and marketing tools means every new lead you add to your CRM can automatically appear in your mailing list. This removes manual updates and keeps all your tools in sync.
There are three main ways SaaS integrations usually work:
- Native integrations
Built directly into the software (for instance, connecting Slack with Google Drive). - Third-party automation tools
Platforms like Zapier, Make, or Workato connect different apps without coding. - Custom API integrations
Developed in-house for complex, large-scale systems that require full control.
In short, SaaS integrations help businesses create a connected software ecosystem where tools communicate effortlessly. This leads to:
- Fewer manual tasks
- More accurate data
- A single source of truth across all systems
The major types of integrations
Not all integrations work the same way. Depending on your needs and the tools you use, you’ll find several different types of SaaS integrations. Each serves a specific purpose and connects systems in its own way.
Here are the main categories to understand:
- Data integrations
These sync data between tools so that every platform reflects the same information.
Example: When customer details in your CRM automatically update in your billing system. - Process integrations
These link apps that handle different steps of a single workflow.
Example: A lead captured in a form tool triggers a follow-up email through your marketing platform. - Functional integrations
These combine features from multiple tools into one unified experience.
Example: Embedding chat support inside a project management platform. - Third-party integrations
Managed by external services such as Zapier, Make, or Workato, these connect many apps without coding. - Custom API integrations
Created in-house to meet specific business needs, giving full control over how tools communicate and what data they share.
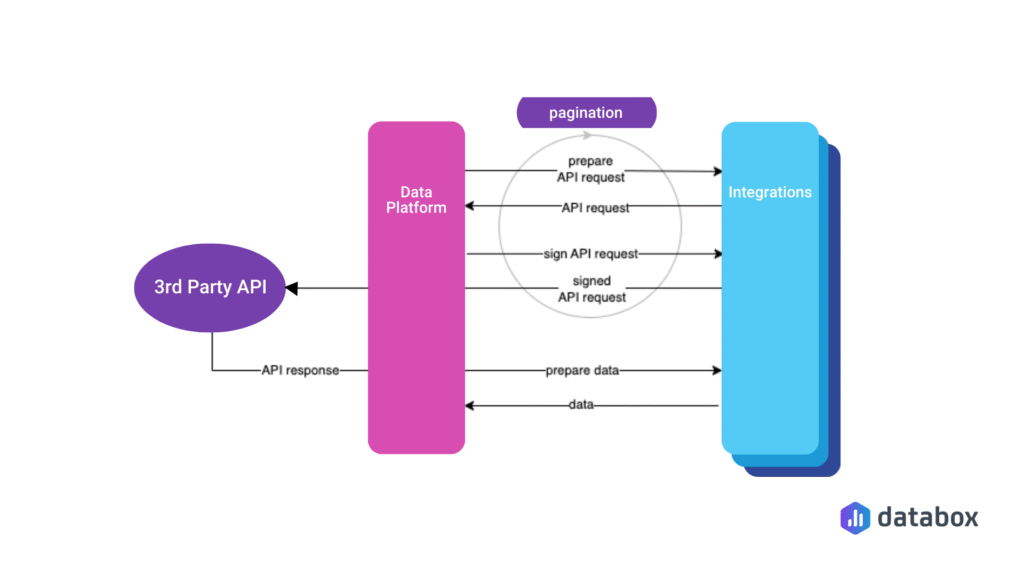
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Main goal | Best for | |
| Data integrations | Keep data consistent across systems | CRMs, analytics, billing tools |
| Process integrations | Automate multi-step workflows | Marketing, sales, HR automation |
| Functional integrations | Combine capabilities from different tools | Support, collaboration, or product apps |
| Third-party integrations | Connect apps quickly without code | Small to medium businesses |
| Custom API integrations | Deep, flexible system connections | Enterprises and technical teams |
The benefits of SaaS integrations for your business
When your software tools work together, your entire operation becomes smoother and more efficient. SaaS integrations eliminate repetitive work, reduce errors, and help your team make faster, data-driven decisions.
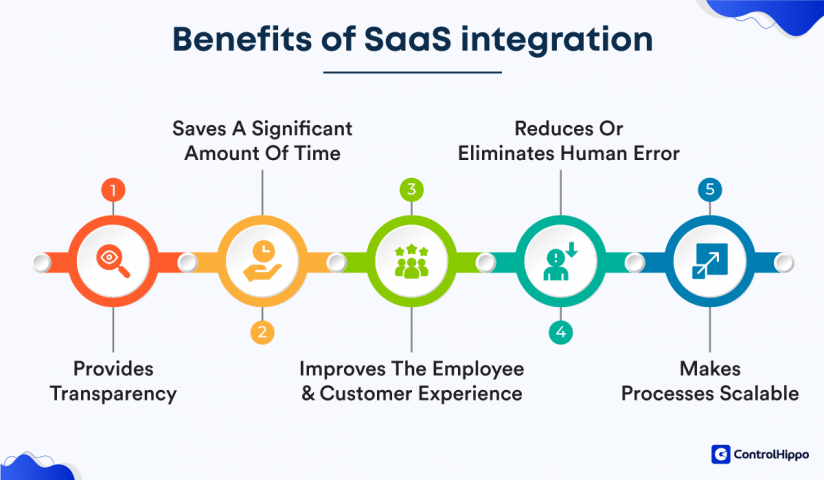
Here are the key benefits of adding integrations to your software stack:
- Better data accuracy
Information stays consistent across platforms, which means fewer manual updates and less room for mistakes. - More efficient workflows
Tasks can trigger automatically between tools. For instance, a new sale in your eCommerce platform can instantly update your CRM and send a confirmation email. - Improved visibility
Integrations create a single, unified view of your business data. This helps teams spot trends and make smarter decisions without jumping between tools. - Higher team productivity
By cutting out repetitive tasks, integrations free up time for more strategic work. Employees can focus on growth instead of admin tasks. - Stronger customer experience
When systems talk to each other, communication and support become faster and more personalized. Customers get quicker responses and better service overall.
In the end, SaaS integrations turn disconnected tools into a single, connected system that supports growth, accuracy, and better decision-making.
The challenges of SaaS integrations
Integrations make life easier, but they aren’t without their pitfalls. The more apps a company connects, the more moving parts it has to manage. Some challenges are technical, while others come down to process and upkeep.
1. Keeping data consistent
Data mismatches are one of the biggest issues. When tools sync at different times or have conflicting data fields, information can get duplicated or lost. Regular audits and clear data ownership rules help prevent this.
2. Managing security and permissions
Every integration opens a new door to your system. If permissions aren’t carefully managed, sensitive data might pass through channels it shouldn’t. Using encryption, access controls, and reviewing connected apps regularly keeps things safe.
3. Balancing simplicity with customization
Not every integration is plug-and-play. Some need custom API connections, which take time and technical skill to set up. The challenge is finding the right balance between convenience and flexibility.
4. Handling downtime and updates
If one connected app changes its API or experiences an outage, it can affect all dependent workflows. Monitoring tools and having backup procedures are key to avoiding unexpected interruptions.
5. Preventing tool sprawl
As teams adopt more apps, integrations can multiply quickly. What started as a few helpful connections can turn into a web of dependencies that’s hard to track or maintain.
To stay ahead of these problems:
- Audit your integrations quarterly.
- Document every connection and its purpose.
- Assign one person or team to oversee integration health.
In short, integrations only work as well as they’re managed. A thoughtful setup today saves you from tangled systems tomorrow.
How do SaaS integrations typically work?
At a high level, SaaS integrations allow different applications to communicate through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). APIs act as translators that let systems share data securely and consistently.
Here’s how the process usually works:
- Authentication
Before two systems can share data, they must confirm they trust each other. This usually happens through API keys or OAuth, which verify access rights without exposing passwords. - Data mapping
Each app structures its data differently. Integration tools match the fields from one system to another, such as aligning “First Name” in your CRM with “Customer Name” in your email platform. - Data transfer
Once mapped, the integration sends and receives data through API calls. This can happen instantly (real-time sync) or at set intervals (batch sync). - Event triggers
Many integrations rely on triggers, like “new lead created” or “invoice paid.” When the event occurs, the connected system automatically performs the next action. - Error handling and logging
If something goes wrong, such as a failed data sync, the integration logs the issue and notifies the user or developer so it can be fixed quickly.
In simple terms, SaaS integrations act like digital bridges, constantly passing information between tools so your systems stay in sync without manual effort.
Examples and use cases of SaaS integrations
SaaS integrations are everywhere — from simple marketing automations to complex enterprise workflows. They help teams connect data, reduce repetitive work, and make different tools act as one coordinated system.
Here are some real-world examples and use cases that show how businesses apply integrations across departments:
1. Marketing and sales alignment
Connecting tools like HubSpot, Salesforce, and Google Ads allows marketing data to flow straight into the CRM.
- Leads from ad campaigns automatically appear in the sales pipeline.
- Sales reps can see where each lead came from and which campaign converted them.
- Marketing teams can measure ROI directly from CRM data.
2. Finance and billing automation
Tools such as QuickBooks, Stripe, or Chargebee integrate with CRMs or eCommerce platforms to simplify financial operations.
- Every customer purchase creates an invoice automatically.
- Payment status updates sync across systems in real time.
- Accounting reports stay accurate without manual reconciliation.
3. Customer support and product data
Support platforms like Zendesk or Intercom can connect with project management tools such as Jira or ClickUp.
- A customer ticket can automatically create a new issue for the product team.
- When the bug is fixed, the support agent gets notified instantly.
4. Internal communication and task management
Integrating Slack, Asana, or Notion keeps teams aligned on projects.
- Slack notifications trigger when a new task is assigned or completed.
- Meeting notes in Notion automatically create related tasks in Asana.
5. HR and employee onboarding
Platforms like BambooHR, Gusto, and Google Workspace work together to simplify onboarding.
- Once a new hire is added to the HR system, accounts and access permissions are created across other tools automatically.
Whether it’s automating sales updates or syncing support tickets with development tasks, SaaS integrations help teams work in sync instead of in silos.
Wrapping up
SaaS integrations have become an essential part of how modern businesses operate. They turn disconnected software into a unified ecosystem where data moves freely and workflows happen automatically. Whether it’s syncing leads between marketing and sales, connecting billing with your CRM, or keeping customer data consistent across tools, integrations make everyday work faster and more reliable.
However, the real value of SaaS integrations is clarity. When systems share data in real time, teams gain a single source of truth that supports smarter decisions and better collaboration.
The key is to start small, connect the tools that matter most, and build from there. With the right setup, SaaS integrations can help any organization work more efficiently and focus on what really drives growth.
FAQs about SaaS integrations
What is the main purpose of SaaS integrations?
SaaS integrations allow different cloud-based tools to exchange data and trigger actions automatically. Their purpose is to reduce manual work, keep information consistent across platforms, and help teams operate from a unified system.
Are SaaS integrations only for large companies?
Not at all. Even small teams benefit from connecting their software tools. Automating tasks like syncing contacts, tracking invoices, or updating leads can save hours each week regardless of company size.
Do I need coding skills to set up a SaaS integration?
In many cases, no. Many modern apps offer native integrations or use platforms like Zapier or Make that let you create connections with simple workflows. For more complex setups, technical teams can use APIs for full customization.
What’s the difference between native and custom integrations?
A native integration is built directly into the app and ready to use, while a custom integration is developed manually using APIs. Native integrations are faster to set up, but custom ones provide more flexibility and control.
How can I make sure my integrations are secure?
Choose tools that use encrypted connections, limit data access through permissions, and regularly review which apps have integration rights. Monitoring API activity also helps catch any irregular data transfers early.
What should I do if an integration stops working?
Check for API changes or authentication issues first. If you’re using a third-party automation platform, review task history to find the failure point. Keeping documentation and version control in place helps restore connections quickly.
How many integrations are too many?
There’s no fixed number, but as a rule, every integration should serve a clear purpose. If connections start overlapping or creating duplicate data, it’s time to review and simplify your setup.
What’s the biggest benefit of having well-structured integrations?
A strong integration setup saves time, improves data accuracy, and gives your team a complete view of your business operations — all without switching between multiple tools.