The software-as-a-service (SaaS) industry has reshaped how companies buy and sell software. Instead of purchasing licenses or installations, customers subscribe to products they can access instantly through the cloud. This shift has created an entirely new way of selling: SaaS sales.
In SaaS, sales teams are not only responsible for closing deals but also for building ongoing relationships that drive renewals, upsells, and long-term growth. Unlike traditional sales, success depends on how well the customer continues to use and value the product over time.
This guide breaks down what SaaS sales really mean in 2025, how it differs from older sales models, and the strategies that make it successful. You’ll learn about the most common SaaS sales models, how to structure your team, and which metrics and tools to track.
What is SaaS sales?
SaaS sales refers to the process of selling software that is delivered and accessed online rather than installed locally on a device. Instead of a one-time purchase, customers typically pay a recurring subscription fee to use the product.
This model focuses on building long-term customer relationships rather than one-off transactions. Sales teams are responsible not only for closing deals but also for renewals, upsells, and customer retention.
SaaS sales professionals often interact with clients through online demos, free trials, and email communication rather than in-person meetings. This makes product knowledge, clear communication, and understanding customer pain points essential.
There are several stages in the SaaS sales process:
- Lead generation: identifying potential customers through marketing or outbound efforts
- Qualification: confirming the prospect’s fit, budget, and needs
- Product demo or trial: showing the software’s value in action
- Negotiation and closing: finalizing pricing and contract terms
- Onboarding and retention: ensuring customer success and long-term satisfaction
SaaS sales require a mix of consultative selling skills, product expertise, and data-driven decision-making, as success depends on maintaining ongoing customer engagement.
SaaS sales models explained
SaaS companies use different sales models depending on their target customers, product complexity, and pricing strategy. The right model helps balance customer acquisition costs with lifetime value, ensuring sustainable growth.
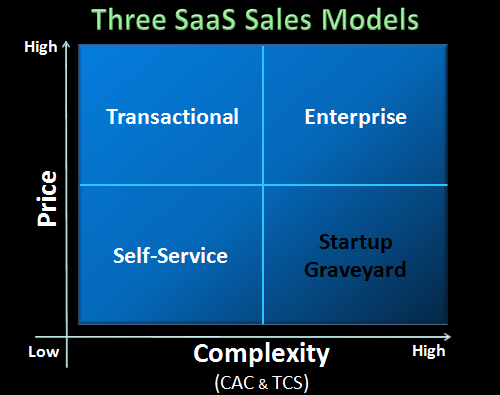
Here are the main SaaS sales models:
| Sales model | Description | Typical customer type | Example pricing style |
| Self-service | Customers sign up, try, and buy without interacting with a salesperson. Works best for simple, affordable products. | Individuals or small teams | Free plan, low-cost monthly subscription |
| Transactional | A mix of automation and human support. Sales reps handle leads that need some guidance before purchasing. | Small to midsize businesses | Tiered plans with optional demos |
| Enterprise | High-touch, customized sales cycle with multiple decision-makers involved. Often includes contract negotiation. | Large corporations or government clients | Custom pricing and long-term contracts |
| Channel/partner sales | Third-party resellers, consultants, or affiliates sell on behalf of the SaaS provider. | Regional markets or niche industries | Commission-based or revenue share |
Each model comes with trade-offs. Self-service models scale quickly but rely heavily on marketing and product-led growth. Enterprise models bring higher revenue per customer but require longer sales cycles and more resources.
Successful SaaS companies often combine models, such as offering a self-service entry point and upgrading users through a sales-assisted or enterprise motion once their needs grow.
How is SaaS sales different from traditional sales models?
SaaS sales stand apart from traditional sales because the product is subscription-based, digital, and constantly evolving. Instead of a one-time transaction, success depends on maintaining customer satisfaction over time.
Here are the main differences:
| Aspect | SaaS sales | Traditional sales |
| Payment structure | Recurring subscription (monthly or yearly) | One-time purchase |
| Customer relationship | Continuous engagement focused on renewals and expansion | Ends after the sale is completed |
| Sales cycle | Often shorter for low-touch products but ongoing post-sale | Fixed and ends after closing |
| Product delivery | Accessed via cloud, with automatic updates | Delivered physically or through local installation |
| Revenue focus | Measured by monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and churn | Measured by total contract value (TCV) |
| Team collaboration | Requires close coordination between sales, marketing, and customer success | Primarily sales-driven |
SaaS sales teams need to think long-term. Customer retention, product adoption, and lifetime value matter more than the initial deal size.
In this model, sales representatives act as consultants who guide prospects through onboarding and continued use, ensuring they achieve measurable results that justify their subscription.
Unique benefits of the SaaS sales model
The SaaS sales model offers several advantages that make it attractive to both companies and customers. Its subscription-based structure encourages ongoing relationships and predictable revenue growth.
1. Recurring and predictable revenue
Instead of one-off transactions, SaaS businesses earn steady income through monthly or annual subscriptions. This allows better forecasting and long-term financial stability.
2. Strong customer relationships
Because success depends on renewals, sales teams focus on delivering continuous value. Customers receive regular updates, new features, and dedicated support, which deepens trust over time.
3. Scalable sales process
Most SaaS tools are delivered online, so businesses can reach global customers without physical limitations. Self-service signups and automation help scale efficiently as demand grows.
4. Easier upselling and cross-selling
With a clear view of user activity and product engagement, sales teams can identify the right moment to offer upgrades or add-ons, increasing customer lifetime value.
5. Data-driven decision-making
SaaS sales rely heavily on analytics. Teams can track user behavior, churn rates, and conversion metrics to refine their approach and improve performance over time.
Overall, the SaaS model aligns business growth with customer success, creating a cycle where both sides benefit continuously.
The SaaS sales process explained
The SaaS sales process focuses on guiding potential customers from first contact to long-term subscription. It blends traditional sales methods with ongoing customer engagement since success depends on retention and renewals.
Here’s how it typically works:
1. Lead generation
Sales and marketing teams attract prospects through content marketing, ads, partnerships, or referrals. The goal is to generate qualified leads who show interest in the product.
2. Lead qualification
Leads are assessed based on fit, need, budget, and readiness to buy. Tools like CRM software or lead scoring systems help prioritize who to contact first.
3. Product demo or free trial
This is where potential customers experience the value of the product. Sales reps or onboarding specialists conduct live demos or offer self-service trials to highlight key features and use cases.
4. Proposal and negotiation
Once the prospect sees the value, the focus shifts to pricing, contract terms, and implementation details. Transparency and responsiveness at this stage help build trust.
5. Closing the deal
Contracts are signed, payment details are confirmed, and onboarding begins. In SaaS, closing is the start of the customer relationship.
6. Onboarding and customer success
Customer success teams help users adopt the product quickly and achieve early wins. Smooth onboarding reduces churn and increases satisfaction.
7. Retention and expansion
SaaS sales don’t stop at the first payment. Sales teams track engagement data to identify upsell or cross-sell opportunities and secure renewals at the end of each cycle.
A successful SaaS sales process is continuous, focusing on long-term relationships, data-driven insights, and customer value rather than one-time conversions.
How to build a SaaS sales team (roles to hire)
Building an effective SaaS sales team means hiring roles that cover every stage of the customer journey, from lead generation to retention. Each position plays a specific part in attracting, converting, and supporting customers.
Here are the key roles to include:
| Role | Main responsibilities | Key skills |
| Sales Development Representative (SDR) | Reaches out to prospects, qualifies leads, and books meetings for account executives. | Communication, research, lead qualification |
| Account Executive (AE) | Manages demos, negotiations, and deal closing. Works directly with qualified leads to turn them into customers. | Persuasion, product knowledge, and objection handling |
| Customer Success Manager (CSM) | Ensures customers are successful after purchase, helping reduce churn and identify upsell opportunities. | Relationship management, problem solving, empathy |
| Sales Manager / Team Lead | Oversees the sales pipeline, sets goals, coaches the team, and ensures alignment with company objectives. | Leadership, analytics, strategic thinking |
| Sales Operations / RevOps Specialist | Manages tools, CRM data, and reporting. Helps improve efficiency and maintain accurate forecasts. | Data analysis, CRM management, process optimization |
Key SaaS sales metrics to track
Tracking the right metrics helps SaaS teams understand performance, forecast revenue, and identify opportunities for improvement. Since recurring revenue is central to this model, the focus is on growth, retention, and customer lifetime value rather than one-off deals.
Here are the most important SaaS sales metrics:
| Metric | What it measures | Why it matters |
| Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) | Total predictable revenue earned every month from active subscriptions. | Shows the company’s financial stability and growth rate. |
| Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) | MRR multiplied by 12, representing yearly predictable income. | Helps evaluate long-term revenue trends. |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | The average cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses. | Indicates efficiency and profitability of your sales efforts. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | The total revenue a company expects to earn from one customer over time. | Helps determine how much you can afford to spend on acquisition. |
| Churn Rate | The percentage of customers or revenue lost during a given period. | Reveals retention problems and product satisfaction issues. |
| Conversion Rate | The ratio of leads that become paying customers. | Highlights how well your team converts interest into sales. |
| Expansion Revenue | Additional revenue from existing customers through upsells or add-ons. | Reflects account growth and customer satisfaction. |
Top tools to help you crush your SaaS sales goals
Hitting SaaS sales targets requires the right mix of technology. The best sales teams use tools that automate repetitive work, organize customer data, and give visibility into performance. Rather than focusing on specific products, here are the key categories of tools every SaaS sales team should consider.
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
A CRM is the foundation of any sales operation. It helps you track leads, manage pipelines, and maintain visibility over the customer journey. CRMs also support collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer success teams.
2. Sales engagement platforms
These tools automate outreach through personalized email sequences, call tracking, and follow-up reminders. They help SDRs stay consistent while managing large lead lists efficiently.
3. Lead generation and enrichment tools
Finding qualified prospects is easier with databases and enrichment platforms that provide accurate contact information, firmographics, and intent data. This ensures your outreach targets the right people.
4. Sales analytics and reporting tools
Analytics software gives insight into metrics like conversion rates, churn, and deal velocity. It helps leaders make data-driven decisions and forecast growth accurately.
5. Proposal and e-signature tools
To speed up deal closing, sales teams use digital tools for creating proposals, managing quotes, and collecting signatures electronically, reducing friction in the final stages of the sales cycle.
6. Customer success and onboarding tools
After the sale, these platforms help monitor usage, manage renewals, and improve customer satisfaction. They’re essential for retaining customers and increasing lifetime value.
7. Communication and collaboration tools
Chat, video conferencing, and internal messaging tools help teams stay aligned and communicate effectively, especially in distributed SaaS companies.
When combined, these categories form a complete sales tech stack that supports every stage of the SaaS customer lifecycle, from prospecting to renewal.
Wrapping up
SaaS sales are built around relationships, not one-time deals. Success comes from delivering ongoing value, understanding customer needs, and using data to make informed decisions at every stage of the sales cycle.
A well-structured SaaS sales process helps teams attract the right prospects, close deals efficiently, and retain customers for the long term. With the right mix of people, strategy, and technology, businesses can build predictable revenue streams and stronger customer loyalty.
As the SaaS market continues to evolve in 2025, the most successful sales teams will be those that stay adaptable, using automation, insights, and customer feedback to improve continuously.
Whether you’re starting from scratch or optimizing an existing sales operation, remember that sustainable growth in SaaS sales comes from consistency, collaboration, and customer success.